gravimetric method blood loss estimation|Comparison of common perioperative blood loss estimation : distribute The bias for estimated blood loss (ml) was lowest for colorimetric methods (57.59 95% CI 23.88-91.3) compared to the reference, followed by gravimetric (326.36 95% CI 201.65-450.86) and . Resultado da 23 de ago. de 2022 · Dragon Ball Z – Budokai Tenkaichi 3 – PS2 PTBR. O jogo possui mais de 150 personagens .
{plog:ftitle_list}
17 de jan. de 2024 · Qual melhor horário parar jogar Fortune OX? Melhor horário para jogar Fortune OX de manhã; Melhor horário para jogar Fortune OX de tarde; Melhor .
The bias for estimated blood loss (ml) was lowest for colorimetric methods (57.59 95% CI 23.88–91.3) compared to the reference, followed by gravimetric (326.36 95% CI 201.65–450.86) and visual methods (456.51 95% CI 395.19–517.83) (Table 2).Estimated blood loss values derived from formula-based techniques were higher than those derived from gravimetric techniques, a finding observed in all six studies. All six studies . Our study assesses the accuracy of intraoperative blood loss measurement using the Triton system and those methods that are used mostly in clinical practice, especially the . The mean blood loss estimated using the gravimetric method was 513.7 ± 421.7 mL, while estimates calculated using the CRYS 3.5, CRYS 1.5 and traditional equations were .
The bias for estimated blood loss (ml) was lowest for colorimetric methods (57.59 95% CI 23.88-91.3) compared to the reference, followed by gravimetric (326.36 95% CI 201.65-450.86) and .
The bias for estimated blood loss (ml) was lowest for colorimetric methods (57.59 95% CI 23.88–91.3) compared to the reference, followed by gravimetric (326.36 95% CI .
The aim of this study was to compare several methods of blood loss quantification-visual estimation by surgeon and anesthesiologist, the gravimetric method, the calculation .
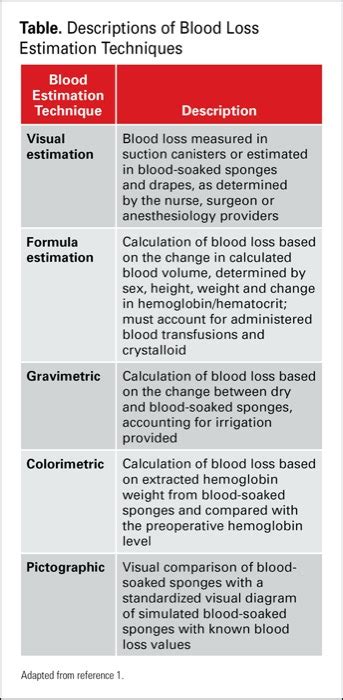
It describes the primary methods for determining blood loss, including visual assessment, photometric analysis, gravimetric blood loss determination, blood loss .Download Citation | On Jan 1, 2023, ChukwudiR Osakwe and others published Accuracy of gravimetric method of blood loss estimation during open myomectomy | Find, read and cite all the research you .
Blood loss estimation is a patient quality-of-care and patient-safety measure and requires a high degree of accuracy. Currently there is no practical, real-time blood loss estimation method for measuring blood loss. Techniques vary across specialties and. Purpose Estimated blood loss (EBL) is an important tool in clinical decision-making and surgical outcomes research. It guides perioperative transfusion practice and serves as a key predictor of short-term perioperative risks and long-term oncologic outcomes. Despite its widespread clinical and research use, there is no gold standard for blood loss estimation. .
Background: Blood loss during major abdominal surgery is an essential parameter in the evaluation of strategies aimed at reducing perioperative bleeding. However, blood loss quantification remains unreliable and inaccurate. The aim of this study was to compare several methods of blood loss quantification-visual estimation by surgeon and anesthesiologist, the .
Overall, the evidence in this review is insufficient to support the use of one method over another for blood loss estimation after vaginal birth. In general, the quality of evidence for our predefined outcomes ranged from low to high quality, with downgrading decisions due to imprecision. The includ . Blood loss during major abdominal surgery is an essential parameter in the evaluation of strategies aimed at reducing perioperative bleeding. However, blood loss quantification remains unreliable and inaccurate. The aim of this study was to compare several methods of blood loss quantification—visual estimation by surgeon and anesthesiologist, . The original study compared visually estimated blood loss, gravimetric QBL, and a colorimetric blood loss estimation to a reference hemoglobin extraction assay during scheduled cesarean delivery. This secondary analysis is focused on the relationship between gravimetric QBL and the reference hemoglobin assay. . The gravimetric QBL method was .
Our objective was to assess the accuracy of gravimetric estimation of intraoperative blood loss using the colorimetric method. Forty laparotomy sponges were selected randomly from general gynecology cases during a 2 month period. The blood contained on each sponge had been assessed by the OR staff b . The bias for estimated blood loss (ml) was lowest for colorimetric methods (57.59 95% CI 23.88–91.3) compared to the reference, followed by gravimetric (326.36 95% CI 201.65–450.86) and visual .The gravimetric method of determining blood loss requires weighing surgical sponges before and after use. The difference in weight is assumed to be the volume of blood lost as measured in milliliters. . Mainland J. F. A simple photo-electric method for the estimation of blood loss during surgery. British Journal of Anaesthesia. 1966;38(1):76 .
Purpose: Among various methods for estimating blood loss, the gravimetric method is the most accurate; however, its use in routine practice is complicated. Although several equations have been proposed for this purpose, there is no consensus on the most suitable. Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted in seven secondary and tertiary hospitals between March .Although one study demonstrated improved accuracy with visual estimation of blood loss through a training program 37, a more recent study demonstrated skill decay within 9 months of training completion 34. Furthermore, visual estimation of blood loss does not appear to improve with health care provider specialty, age, or clinical experience 14 .Comparison between the three methods of blood loss calculation was carried out. Results: A total of 150 patients were included in this study. There was a significant difference between the gravimetric calculated blood loss and both health-care providers' estimation with a tendency to underestimate the loss by about 30%. Comparison between the three methods of blood loss calculation was carried out.ResultsA total of 150 patients were included in this study. There was a significant difference between the gravimetric calculated blood loss and both health-care providers’ estimation with a tendency to underestimate the loss by about 30%.
Objectives: The aim of the study was to estimate postpartum blood loss visually and by gravimetric method and compare the both. Methods: This study was conducted in the Department of Obstetrics . Purpose One of the major problems in international literature is how to measure postpartum blood loss with accuracy. We aimed in this research to assess the accuracy of visual estimation of postpartum blood loss (by each of two main health-care providers) compared with the gravimetric calculation method. Methods We carried out a prospective cohort study at .Estimating intraoperative blood loss is one of the daily challenges for clinicians. . and finally visual methods (0.61 95% CI 0.40-0.82). The bias for estimated blood loss (ml) was lowest for colorimetric methods (57.59 95% CI 23.88-91.3) compared to the reference, followed by gravimetric (326.36 95% CI 201.65-450.86) and visual methods (456. . Visual estimation is not optimal for measurement of postpartum blood loss in PPH and should be withdrawn from standard obstetric practice and replaced with objective measurement using the sterile under-buttock drape. INTRODUCTION Immediate postpartum haemorrhage (PPH) is the most common cause of maternal mortality worldwide. Most .
There are several methods or technologies used to estimate blood loss (EBL) or Hb loss (EHL) during surgery , such as the visual method, gravimetric method and, recently, new methods based on computer algorithms (3-6). . Visual estimation remains the standard of care in estimating blood loss, yet is demonstrably inaccurate. Photometric analysis, which is the referenced “gold-standard” for measuring blood loss, is both time-consuming and costly. . (EBL) from the Triton system were compared with the estimates of blood loss via the gravimetric method and .
The study suggests a real and significant difference in blood loss measurement between these methods. Research using blood loss measurement as an endpoint needs to be interpreted taking measurement technique into consideration. . Visual estimation versus gravimetric measurement of postpartum blood loss: a prospective cohort study. Arch .
The various methods commonly used to estimate the blood loss are the visual estimation of the blood loss, use of a funnel-shaped drape with an attached plastic sheet placed underneath the buttocks .The gravimetric estimation of blood loss is an objective method that includes sensitive weighing of the lost blood collected as well as materials such as soaked pads, gauze and others. . The correlation between the diVerent methods of blood loss estimation and maximum hemoglobin drop after delivery was also calculated. Moreover, we calculated .Visual estimation of postpartum blood loss, a simple and convenient method, has been a routine practice for a long time, even though some researchers have claimed that this method is inaccurate and results in the underestimation of the actual volume of blood loss.(4-7,9) Simulation training to improve visual estimation has not resulted in an . Objectives: The aim of the study was to estimate postpartum blood loss visually and by gravimetric method and compare the both. Methods: This study was conducted in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, GMC Amritsar on 100 pregnant women satisfying the inclusion criteria over a period of 1.5 years. Patient’s consent was taken and visual estimation .
Methods for measuring blood loss are often complex, vague or difficult to implement in clinical practice, and they tend to differ across institutions, disciplines and among individual health care providers. . (Figure), and gravimetric-based estimation incorporating changes in the dry and wet weight of surgical sponges. Figure.Gravimetric evaluation of intraoperative blood loss was found to be an accurate method, which can be recommended for use in a clinical setting. Clinical relevance: Estimation of blood loss using a gravimetric method is accurate and applicable in the clinical setting and provides surgeons with a simple and objective tool to evaluate .
speed test drops out
Marketing, Sales, and Customer Service teams save time and cut operating costs by automating conversations with Landbot's AI Chatbot Generator.
gravimetric method blood loss estimation|Comparison of common perioperative blood loss estimation